Only after the company fulfills its obligations will the revenue be recognized on the income statement. This avoids overstatement of income and ensures accurate timing of revenue recognition. Unearned revenue is classified as a liability because it reflects an obligation to the customer.

We and our partners process data to provide:
It is never recognized immediately because of contractual obligations or accounting principles. Unearned revenue and deferred revenue are crucial for accurately recognizing revenue. Unearned revenue refers to the advance payment the company receives for offering goods and services.
- If you have earned revenue but a client has not yet paid their bill, then you report your earned revenue in the accounts receivable journal, which is an asset.
- Earned revenue means you have provided the goods or services and therefore have met your obligations in the purchase contract.
- You record it under short-term liabilities (or long-term liabilities where applicable).
- If the consideration received exceeds the fair value of the goods or services provided, the excess should be recognized as a liability or deferred income.
- Each time a portion of the service or product is delivered, the accountant makes a journal entry moving the appropriate amount from unearned revenue to a revenue account on the income statement.
- Trust is needed because it is rare for money and goods to exchange hands simultaneously.
Why is it important to record unearned revenue on the balance sheet?
- Unearned Revenue refers to customer payments collected by a company before the actual delivery of the product or service.
- The table below shows how each one affects when revenue is recorded and how it appears on financial statements.
- Creating and adjusting journal entries for unearned revenue will be easier if your business uses the accrual accounting method when recording transactions.
- In your books, unearned revenue sits on your balance sheet as a „current liability“ – basically, it’s a reminder that you owe your customer something.
Unearned revenue, also known as deferred revenue, refers to funds a company receives from customers for goods or services yet to be delivered. This prepayment represents a liability on the company’s balance sheet because it signifies an obligation Outsource Invoicing to fulfill future performance. Recording unearned revenue involves a two-step process in accounting.
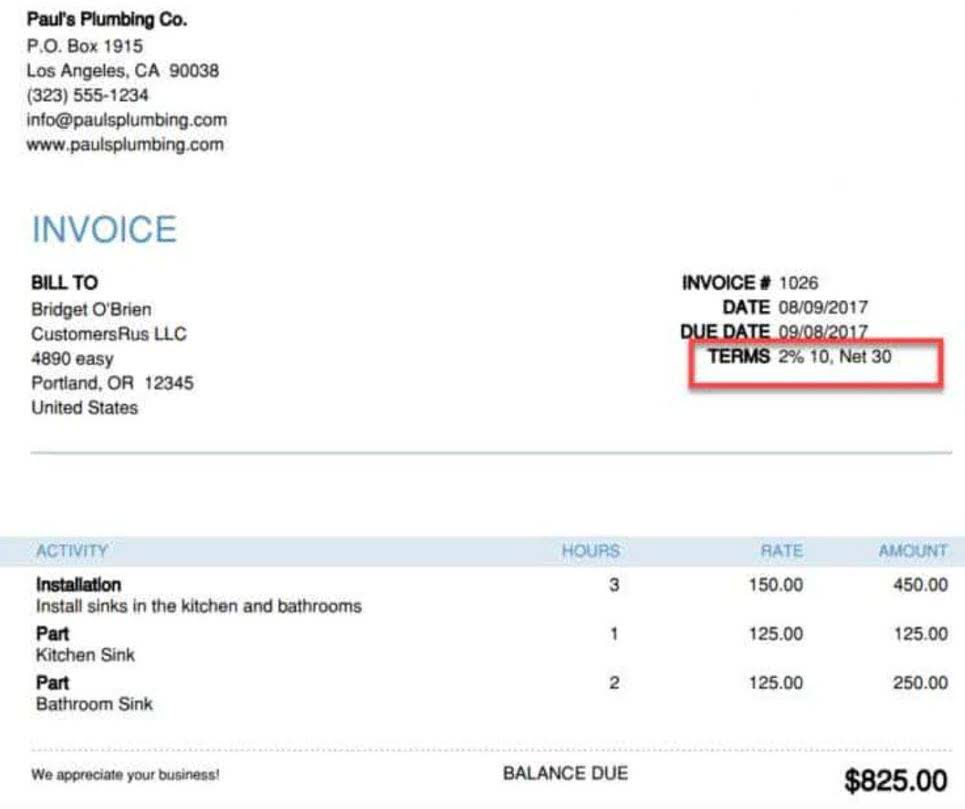
How to account for unearned revenue on financial statements

As compared to revenue recognition, they will have to create a liability account for the unearned revenue. I’m not sure exactly what your question is, but if a company has unearned revenue, they will debit cash and credit the unearned revenue liability. When the revenue is finally earned, the liability is debited and revenue (which goes through retained earnings) is credited.
Be ready for tax time

This deferring of revenue to the periods in which it is earned will often be recorded by using the liability account Deferred Revenues. The monthly entry for $2,000 is often described as a deferral adjusting entry. At the https://www.cqcinvestigations.co.uk/oregon-tax-tables-2023-tax-rates-and-thresholds-in-2/ end of the second quarter of 2020, Morningstar had $287 million in unearned revenue, up from $250 million from the prior-year end. The company classifies the revenue as a short-term liability, meaning it expects the amount to be paid over one year for services to be provided over the same period. Unearned revenue represents payments that a business receives for goods and services that have not yet been delivered. Unearned revenue can provide a financial cushion for a company to explore growth opportunities.
Journal entry for cash received for services not yet performed
It is the revenue that has not yet been received from the client after delivering goods or services. A company cannot immediately what is unearned revenue recognize the cash proceeds received in advance as revenue because it is against the guidelines of the IFRS 15, which deals with revenue recognition. Because of this prepayment, the seller has a liability equal to the unearned revenue or the cash received from the payer. Unearned revenue is considered as prepayment by the payer for which they still have to receive the services or goods. Unearned revenue is the amount that the supplier receives in advance from a customer for which the goods or services are not supplied to or satisfied by the customers.